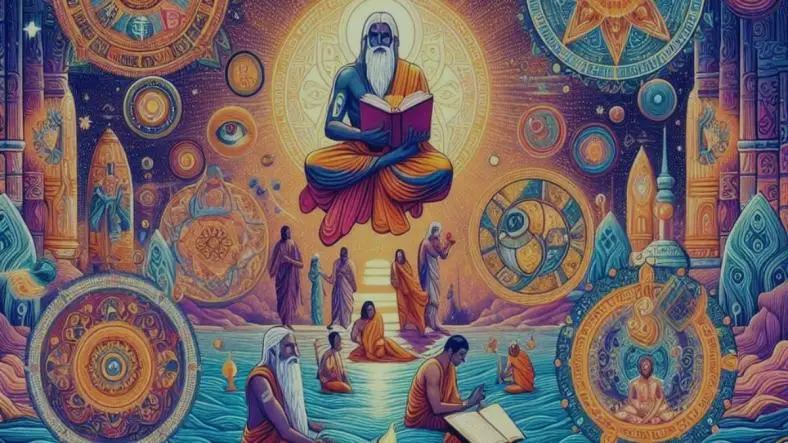
The Vedas are the most ancient and sacred scriptures of Hinduism. Composed in early Sanskrit more than 3,000 years ago, they are not just old religious texts but living sources of philosophical, spiritual, and cultural wisdom. Even today, the Vedas continue to shape Hindu beliefs, rituals, values, and identity. Their teachings influence daily practices, temple traditions, and the broader worldview of millions of Hindus.
This expanded article explores the historical background of the Vedas, their structure, and their deep connection to modern Hindu life.
Historical Background of the Vedas
Ancient Origins
The Vedas consist of four foundational texts:
- Rigveda – Hymns praising various deities
- Samaveda – Melodic chants used in rituals
- Yajurveda – Ritual formulas and ceremonial guidelines
- Atharvaveda – Hymns, prayers, and everyday philosophies
These texts were composed between 1500–500 BCE, during the early Vedic period. For centuries, they were preserved through a strict oral tradition. Vedic scholars memorized the texts word-for-word, ensuring flawless transmission from one generation to the next. This oral tradition is one of the most precise in human history.
Scriptural Authority
The Vedas are classified as śruti, meaning “that which is heard.”
This signifies:
- Divine origin
- Highest authority in Hindu tradition
- Primary source of spiritual and philosophical knowledge
Later texts such as the Upanishads, Puranas, Mahabharata, Ramayana, and various Smritis built upon the foundation laid by the Vedas.
Influence of the Vedas on Modern Hindu Practices
Rituals and Ceremonies
Many modern Hindu rituals trace their roots back to the Vedic period:
- Weddings
- Naming ceremonies
- Housewarming (Griha Pravesha)
- Seasonal festivals
- Yajnas and homas
Even though rituals have evolved over centuries, their central structure — recitation of hymns, fire offerings, and invoking blessings — remains deeply Vedic.
Role of Vedic Priests
Vedic priests (purohits) continue to play a crucial role in Indian society. Their responsibilities include:
- Performing ceremonies
- Reciting Vedic mantras
- Guiding families during important life events
- Preserving ritualistic knowledge
Their training is rooted in memorization, pronunciation, and mastery of Vedic chants, helping maintain the authenticity of these ancient traditions.
Impact on Hindu Philosophy and Thought
Key Concepts Introduced in the Vedas
The Vedic texts introduce several ideas that still shape Hindu ethics and beliefs:
- Dharma – Duty, righteousness, moral order
- Rta – Universal order and natural truth
- Karma – The law of cause and effect
- Yajna – The spirit of sacrifice and offering
These concepts have guided Hindu social structure, values, and spiritual life for thousands of years.
Foundation for Vedanta
Vedanta, one of the most influential schools of Hindu philosophy, is based on the Vedic teachings found in the Upanishads. Vedanta explores:
- Brahman – The ultimate reality
- Atman – The eternal self
- The unity between the individual soul and universal consciousness
Modern spiritual leaders, yoga traditions, and philosophical movements draw heavily from Vedantic ideas.
Influence on Later Scriptures
The Upanishads, Bhagavad Gita, and Puranas expand the philosophical principles of the Vedas. Many well-known stories, rituals, and devotional practices have roots in Vedic literature.
Cultural Significance in the Modern World
Preserving Cultural Identity
The Vedas help connect Hindus with their cultural roots. Many modern practices — from daily prayers to major festivals — include Vedic elements. This creates a sense of continuity between the ancient and the modern world.
Education and Research
Traditional Gurukulas and Veda Pathashalas still teach:
- Chanting techniques
- Vedic rituals
- Sanskrit grammar
- Philosophical interpretation
Meanwhile, universities and researchers across the world study Vedic literature to understand ancient Indian knowledge systems, linguistics, astronomy, medicine, and more.
Vedas in a Changing Society
Adapting Rituals to Modern Life
As society becomes faster and more urban, many rituals have been simplified. Shorter pujas, online consultations with priests, and digital learning of mantras help people stay connected with traditions despite busy lifestyles.
This flexibility has helped Vedic culture remain relevant without losing its essence.
Global Influence
Hindu communities around the world continue to follow Vedic practices in temples and homes.
The universal messages of the Vedas — peace, unity, truth, self-realization — have attracted global attention, making them important in interfaith and spiritual discussions.
Concepts like meditation, mantra chanting, and yoga have gained wide acceptance internationally, strengthening the influence of Vedic philosophy.
Conclusion
The Vedas are more than ancient scriptures — they are living texts that continue to guide, inspire, and enrich modern Hinduism. Their influence is visible in rituals, festivals, philosophical thought, and cultural identity. Despite the rapid changes of modern life, the Vedas continue to remain relevant, offering timeless wisdom for spiritual growth and ethical living.
Their enduring presence in temples, homes, and global spiritual conversations shows that the teachings of the Vedas are truly timeless.