Solar energy is becoming one of the most popular sources of clean and affordable electricity. Whether you want to reduce your electricity bill, go eco-friendly, or enjoy long-term savings, installing solar panels is a great choice. But simply buying high-quality solar panels is not enough. The position and placement of your solar panels play a very important role in how much energy you actually get from them.
Many solar installations produce 20–40% less energy just because the panels are not installed correctly. To avoid this loss, homeowners must understand how orientation, tilt, shade, and other factors affect performance.
In this article, we will explain everything in simple, easy-to-understand language. By the end, you will know exactly how to place your solar panels for maximum sunlight, higher output, and better long-term savings.
Why Proper Solar Panel Placement Matters
Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity. The more sunlight they receive, the more power they generate. Proper placement:
- Increases energy production
- Reduces electricity bills
- Improves return on investment (ROI)
- Reduces maintenance issues
- Helps your solar system last longer
A well-planned installation can improve solar output by 30% or more—without changing the number of panels.
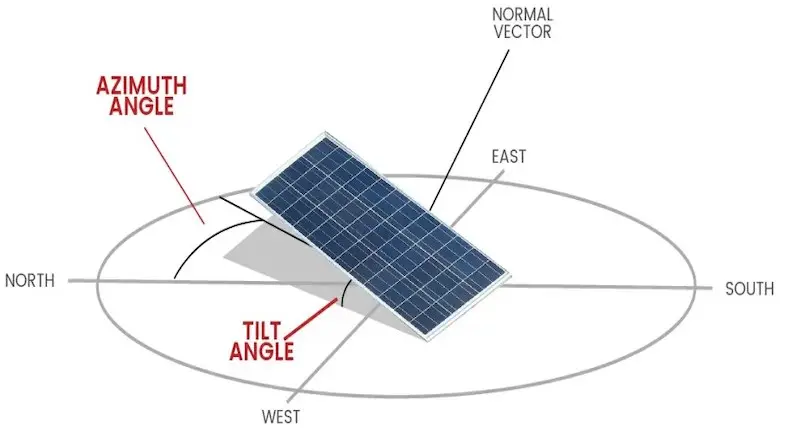
Best Orientation for Solar Panels
1. Northern Hemisphere (India, USA, Europe, etc.)
Solar panels should face true south.
Not magnetic south, but geographic south, which gives the maximum sunlight during the day.
2. Southern Hemisphere (Australia, South Africa, etc.)
Panels should face true north.
Why orientation matters:
Solar panels generate electricity throughout the day as the sun moves from east to west. A north–south alignment ensures that panels capture sunlight during the largest portion of the day.
If your roof is not perfectly aligned, do not worry. Even a slight deviation (up to 30 degrees) still works well. But facing east or west can lead to lower output.
Ideal Tilt Angle for Maximum Efficiency
The tilt angle is the angle between your solar panel and the ground.
1. General rule:
Tilt angle = Your latitude
For example:
- Delhi latitude: ~28° → Tilt = 28°
- Bengaluru latitude: ~13° → Tilt = 13°
- Mumbai latitude: ~19° → Tilt = 19°
This angle ensures your panels capture the most sunlight throughout the year.
2. Seasonal tilt adjustments (optional)
If you want better performance:
- Summer: Reduce tilt by ~10°
- Winter: Increase tilt by ~10°
This is only possible if you have adjustable racks. Roof-mounted fixed systems usually stick to a single optimal angle.
Avoid Shading at All Costs
Shading is one of the biggest enemies of solar energy. Even a small shade—like a tree branch or a cable—can reduce output by 50% or more.
Here are common sources of shading:
- Trees
- Neighboring buildings
- Water tanks
- Chimneys
- Poles, antennas, or solar rails
- Other solar panels in tightly packed installations
Why shading is harmful:
Solar panels are connected in series in many systems. This means one shaded panel can reduce the performance of an entire row.
To avoid this, ensure:
- Your rooftop receives sunlight for at least 5–6 hours per day
- There are no shadows from 9 AM to 3 PM
- Installers perform a shade analysis before installation
Maintain Good Airflow Around Panels
Many people do not realize that panels lose efficiency when they become too hot. High temperatures reduce voltage output.
To prevent heat buildup:
- Leave at least 6–10 cm gap between panels and roof
- Ensure air can flow freely under the panels
- Avoid placing panels directly on metal rooftops
Better cooling = better performance, especially in hot countries like India.
Consider Solar Tracking Systems (Optional but Powerful)
Solar tracking systems automatically rotate solar panels so they follow the sun’s movement.
1. Types of trackers:
- Single-axis: Follows the sun from east to west
- Dual-axis: Adjusts both tilt and direction
2. Benefits:
- Up to 25–40% more energy generation
- Very useful for open-land installations or solar farms
3. Disadvantage:
- Expensive
- Requires maintenance
For homeowners, a fixed system is usually more cost-effective. But for commercial projects, tracking can be an excellent upgrade.
Google Ad 1
Roof Angle and Direction
Every roof is different. Some homes have flat roofs, some have slopes, and some have complex designs.
1. If your roof is flat:
- You can install a racking system to set the perfect tilt (10–25°)
- You can also adjust the angle seasonally
- It gives you maximum flexibility
2. If your roof is sloped:
Try to choose the roof section that:
- Faces true south
- Has a slope angle close to the ideal tilt
- Is free from obstructions
If the slope is not perfect, solar racks can still correct the angle.
Maintain Proper Spacing Between Panels
Panels should not be placed too close to each other. If they are, one panel may cast a shadow on another—especially during mornings or evenings.
Leave enough spacing so that:
- No panel shades another
- Airflow remains strong
- Cleaning and maintenance become easier
Proper spacing improves both efficiency and system lifetime.
Use Shade-Analysis Tools for Accuracy
Solar installers often use professional tools like:
- SunEye
- Solar Pathfinder
- Drone scanning
- Digital modelling software
These tools help predict how much shade your rooftop will get throughout the year. This ensures you get the best placement for your solar panels.
Use Microinverters or Power Optimizers
Traditional systems use a single central inverter. If one panel gets shaded, the entire system performance drops.
Microinverters and power optimizers solve this problem.
Benefits:
- Each panel works independently
- Shading on one panel does not affect others
- Higher overall energy production
- Better monitoring and maintenance
They cost slightly more but give excellent performance, especially on roofs with partial shade.
Always Get a Professional Solar Installation
Solar panels are a big investment. A professional installer can:
- Conduct a site survey
- Perform shade analysis
- Recommend the best direction and tilt
- Use safe wiring and mounting
- Ensure long-term performance and safety
Trying to install solar panels without expert help can lead to:
- Lower power generation
- Fire risks
- Structural damage
- Voided warranties
A good installer ensures maximum efficiency and long-term reliability.
Final Thoughts
Optimal placement of solar panels is the key to getting the most energy from your system. By choosing the right direction, angle, spacing, and avoiding shading, you can significantly increase output and reduce your electricity bill.
To summarize:
- Face panels south (Northern Hemisphere) or north (Southern Hemisphere)
- Use a tilt angle equal to your latitude
- Avoid shading at all times
- Maintain proper spacing and airflow
- Consider microinverters for better performance
- Hire a professional installer for the best results
Solar energy is a long-term investment. With proper planning and placement, your solar panel system can deliver clean, free electricity for 25+ years.
Thank You for Reading! If you enjoyed this article and want more useful content on Science and Technology, renewable energy, and home improvements, read and subscribe to PeoplesBLOG. Your support helps us create more informative articles that benefit everyone.


![OnePlus Pad 2(12.1 Inch)LCD Display,12GB RAM, 256GB Storage,Snapdragon 8 Gen 3,144Hz Refresh Rate,Dolby Vision & Atmos,Open Canvas,AI features,6 speakers,Wi-Fi with Cellular Data Sharing [Nimbus Gray] OnePlus Pad 2(12.1 Inch)LCD Display,12GB RAM, 256GB Storage,Snapdragon 8 Gen 3,144Hz Refresh Rate,Dolby Vision & Atmos,Open Canvas,AI features,6 speakers,Wi-Fi with Cellular Data Sharing [Nimbus Gray]](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/61tslaYWLjL._SX679_.jpg)






![Dell [Smartchoice] Core i3-1215U, 12th Gen (8GB RAM/512GB SSD/FHD/Window 11/MS Office' 21/15"(38 cm)/15 Month McAfee/Black/1.48kg Laptop Dell [Smartchoice] Core i3-1215U, 12th Gen (8GB RAM/512GB SSD/FHD/Window 11/MS Office' 21/15"(38 cm)/15 Month McAfee/Black/1.48kg Laptop](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/61QXAqq9OhL._SX679_.jpg)



