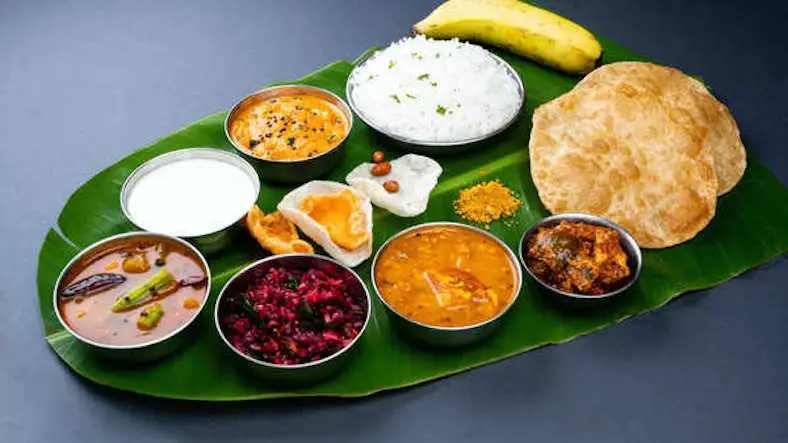
Approximately 30-40% of the population in India is estimated to follow a vegetarian diet. However, this percentage can vary depending on the region, cultural practices and religious beliefs.
Why Indians Follow Vegetarianism:
- Religious Beliefs:
- Hinduism: Many Hindus follow a vegetarian diet as part of their religious beliefs, which promote compassion and non-violence (ahimsa). They believe in the principle of respecting all living beings and abstaining from meat consumption aligns with this philosophy.
- Jainism: Jainism advocates for strict non-violence and compassion towards all living beings. Therefore, Jains predominantly adhere to a vegetarian lifestyle, avoiding not only meat but also root vegetables to minimize harm to plants.
- Cultural Traditions:
- In many Indian communities, vegetarianism is deeply ingrained in cultural traditions and culinary practices. Traditional Indian cuisine offers a wide variety of delicious vegetarian dishes, making it easy for people to adopt a meat-free diet.
- Health Considerations:
- Some Indians choose to follow a vegetarian diet for health reasons, as plant-based diets are associated with numerous health benefits, including reduced risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes and certain cancers.
- Environmental Concerns:
- A growing awareness of environmental issues, including the impact of meat production on climate change, land use and water consumption, has led some individuals to adopt vegetarianism as a way to reduce their environmental footprint.
How Indians Follow Vegetarianism:
- Dietary Choices:
- Vegetarianism in India encompasses a wide range of dietary choices, from lacto-vegetarian diets that include dairy products to vegan diets that exclude all animal products.
- Culinary Diversity:
- Indian cuisine offers a rich diversity of vegetarian dishes, including lentil-based curries (dal), vegetable stir-fries (sabzi), dairy-based desserts (mithai) and fermented rice dishes (dosa, idli).
When Vegetarianism Became Prominent in India:
- Historical Roots:
- Vegetarianism has ancient roots in India, dating back thousands of years. The concept of ahimsa (non-violence) and reverence for all living beings has been central to Indian spiritual and philosophical traditions for millennia.
- Influence of Religious Movements:
- Religious movements such as Hinduism and Jainism have played a significant role in promoting vegetarianism throughout Indian history. These traditions have shaped cultural attitudes towards food and dietary practices.
Overall, vegetarianism is deeply intertwined with the religious, cultural and philosophical fabric of India. While not all Indians follow a vegetarian diet, it remains a prominent dietary choice for millions of people across the country.
Thanks for reading the article, for more food related articles read our peoples blog articles.