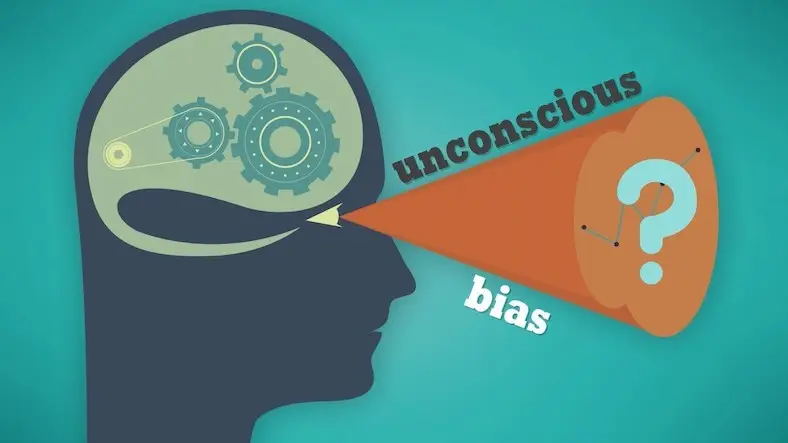
Unconscious biases are automatic and unintentional judgments and attitudes that people hold about others based on characteristics such as race, gender, age, or other social categories. These biases can influence decision-making and behavior in subtle ways.
There are various types of unconscious biases and individuals may harbor multiple biases simultaneously.
Here are some common types:
- Affinity Bias: This bias involves favoring individuals who are similar to oneself in terms of background, experiences, or interests. It can contribute to the formation of cliques and hinder diversity.
- Confirmation Bias: People tend to seek out information that confirms their existing beliefs and opinions, ignoring or dismissing information that contradicts their views.
- Halo Effect: This occurs when an individual's positive traits or characteristics influence the overall perception of that person, leading to an overly positive assessment.
- Horns Effect: The opposite of the halo effect, where negative traits or characteristics overshadow the overall perception of an individual.
- Implicit Association Bias: This bias involves associating certain groups or characteristics with positive or negative stereotypes at an unconscious level. Implicit biases can be measured through tools like the Implicit Association Test (IAT).
- Gender Bias: Biases based on gender can manifest in various ways, such as perceiving certain roles as more suitable for a specific gender or holding stereotypical views about the capabilities of men or women.
- Racial Bias: Bias based on race involves making judgments about individuals or groups based on their racial or ethnic background. This can lead to discriminatory behaviors.
- Ageism: Age-related biases involve making judgments about individuals based on their age. This can affect perceptions of competence, adaptability and relevance.
- Beauty Bias: This bias involves associating physical attractiveness with positive qualities, such as competence or intelligence.
- Conformity Bias: The tendency to adopt the opinions or behaviors of a majority, even if those opinions or behaviors are not well-founded.
- Name Bias: Bias based on names, where individuals may make assumptions about a person's background, socioeconomic status, or personality based on their name.
- Height Bias: The tendency to associate height with qualities such as leadership or authority.
- Disability Bias: Biases against individuals with disabilities, which can manifest in perceptions of capability, competence, or suitability for certain roles.
- Maternity Bias: Bias based on pregnancy or motherhood, where individuals, particularly women, may face discrimination or stereotypes related to their family planning.
- Socioeconomic Bias: Biases based on socioeconomic status can lead to assumptions about an individual's intelligence, work ethic, or values.
- Cognitive Bias: A broad category that includes various biases that affect decision-making processes, such as anchoring bias, availability bias, or confirmation bias.
It's important to note that these biases are not mutually exclusive and individuals may exhibit a combination of biases. Recognizing and addressing unconscious biases is a crucial step toward promoting fairness, equity and inclusivity in various aspects of life, including the workplace, education and social interactions.
Thanks for reading the article, for more lifestyle related articles read our peoples blog articles.












![OnePlus Buds Pro 3 Bluetooth TWS in-Ear Buds - Dual Drivers, Dual DACs, Dynaudio EQs, Up to 50dB Adaptive Noise Cancellation, Up to 43Hrs Battery [Lunar Radiance] OnePlus Buds Pro 3 Bluetooth TWS in-Ear Buds - Dual Drivers, Dual DACs, Dynaudio EQs, Up to 50dB Adaptive Noise Cancellation, Up to 43Hrs Battery [Lunar Radiance]](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/61dVOVxHn3L._SX679_.jpg)

![Dell [Smartchoice] Core i3-1215U, 12th Gen (8GB RAM/512GB SSD/FHD/Window 11/MS Office' 21/15"(38 cm)/15 Month McAfee/Black/1.48kg Laptop Dell [Smartchoice] Core i3-1215U, 12th Gen (8GB RAM/512GB SSD/FHD/Window 11/MS Office' 21/15"(38 cm)/15 Month McAfee/Black/1.48kg Laptop](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/61QXAqq9OhL._SX679_.jpg)